Module 8—Mechanical Waves
 Lesson Summary
Lesson Summary
As you worked through this lesson, you should have developed partial answers to the following questions:
- What happens to the wavelength and frequency of sound that is produced by a moving source?
- How does the Doppler equation describe the frequency observed by a moving sound source?
When the sound source is moving, the leading wave fronts are compressed. According to the universal wave equation, the shortened wavelength will produce a higher frequency sound as it approaches a stationary observer. At the same time, the trailing wave fronts are stretched and the longer wavelength produces a lower frequency sound as the source moves past and away from the observer.
The Doppler effect is the observed change in frequency and wavelength of a wave produced by a moving source relative to an observer. Expressed as an equation, it is
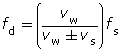
Quantity |
Symbol |
SI Unit |
Doppler frequency (observed) |
fd |
Hz |
source frequency |
fs |
Hz |
wave velocity |
vw |
m/s |
source velocity |
vs |
m/s |
The wave and source velocities are subtracted when the source is moving towards the stationary observer. The velocities are added when the source is moving away from the stationary observer.
Lesson Glossary
Doppler effect: the observed change in frequency and wavelength of a wave produced by a source moving relative to an observer