Module 7—Oscillatory Motion
 Module Summary
Module Summary
At the beginning of this module you were asked to think about the following question:
- What are examples of oscillatory motion in the world around you?
Oscillatory motion is motion in which the period of each cycle is constant.
Simple harmonic motion is a case of oscillatory motion, where the restoring force is proportional to the displacement of the mass relative to the equilibrium position. The displacement and force are always in opposite directions.
The period of a weighted spring is the time required to complete one cycle. It is defined by the spring constant and the mass of the weight attached to the spring. Mathematically, the relationship is expressed by
![]()
The period for simple harmonic motion can be the same as that for circular motion. The radius of the circular motion is identical to the amplitude of the simple harmonic motion.
A pendulum demonstrates simple harmonic motion when the amplitude of the motion is small and the restoring force is proportional to the displacement of the pendulum relative to the equilibrium position. The displacement and force are always in opposite directions.
The restoring force of a pendulum is the component of gravity that acts along the arc to pull the mass back towards the equilibrium position. Mathematically, the relationship is expressed by
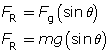
The period of a pendulum is the time required to complete one cycle. It is dependent on the length of the pendulum and acceleration due to gravity. Mathematically, the relationship for small angles is expressed by
![]()
The period for simple harmonic motion can be the same as that for circular motion. The radius of the circular motion is identical to the amplitude of the simple harmonic motion. This fact is observed in the conversion of the simple harmonic motion of a pendulum into the uniform circular motion of the hands on a clock.
Resonant frequency is the natural frequency of vibration for an object, defined by its physical characteristics, such as the length of a pendulum or the shape of a quartz crystal.
Mechanical resonance is the increase in amplitude of oscillation of a system as a result of a periodic force whose frequency is equal to or very close to the resonant frequency of the system.
Buildings, bridges, musical instruments, and clocks are all applications of mechanical resonance. The resonant frequency of such objects must be understood in order for the object to work properly and safely.
 Module 7 Assessment
Module 7 Assessment
The assessment for Module 7 consists of three (3) assignments, as well as a module project:
- Module 7: Lesson 1 Assignment
- Module 7: Lesson 2 Assignment
- Module 7: Lesson 3 Assignment
- Module 7 Project
Module 7 Project
Choose one of the Reflect on the Big Picture activities that best represents your understanding of one of the concepts of this module. Reflect on your work now that you have completed the module, and rework where necessary. Provide reasons as to why and how you made this choice over one of the other Reflect on the Big Picture activities.