Module 7—Oscillatory Motion
 Read
Read
At the start of this lesson, the frequency vibration of guitar strings was mentioned in reference to simple harmonic motion. Then, in the lab, you determined the factors that influence the period and frequency of a weighted spring. Find out how to determine the value of the frequency and period of the mass-spring system by reading pages 373 to 376 in your textbook.
Following are two other examples of how this is done.
Example Problem 2
Calculate the period of oscillation for a 6.00-kg mass hanging on a spring with a spring constant of 75.0 N/m.
Solution

Example Problem 3
A 1.00-kg mass hangs from a spring and oscillates with a frequency of 10.0 Hz. Calculate the spring constant.
Solution
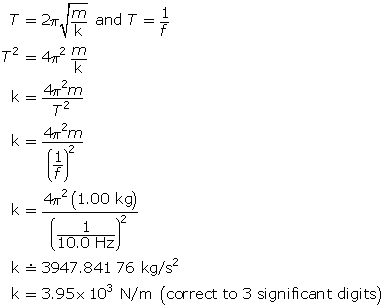
 Self-Check
Self-Check
SC 12. An object hangs from a spring and oscillates with a frequency of 3.50 Hz. If the spring constant is 24.5 N/m, what is the mass of the object?
 Self-Check Answers
Self-Check Answers
SC 12.
Given
f = 3.50 Hz
k = 24.5 N/m
Required
the mass of the object (m)
Analysis and Solution
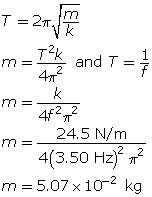
Paraphrase
The object has a mass of 5.07 × 10–2 kg.
 Module 7: Lesson 1 Assignment
Module 7: Lesson 1 Assignment
Remember to submit the answers to TR 4 and TR 5 to your teacher as part of your Module 7: Lesson 1 Assignment.
TR 4. A 78.5-kg man is about to complete a bungee jump. If the bungee cord has a spring constant of 150 N/m, determine the period of oscillation that he will experience.
TR 5. A 5.00-kg mass oscillates on a spring with a frequency of 0.667 Hz. Calculate the spring constant.