Module 6—Work and Energy
Kinetic Energy
kinetic energy: energy that a body has because of its motion
Expressed as an equation, it is
![]()
From the moment the jumper steps off the bridge or platform until the bungee cord starts to stretch, the jumper experiences free fall (weightlessness, assuming no air resistance). During this time period, the jumper’s gravitational potential energy is converted into kinetic energy (energy of motion). He or she accelerates downward at the rate of gravity, gaining considerable speed and kinetic energy until the bungee cord stretches far enough that the restoring force exceeds the force of gravity. At that point, the net acceleration reverses direction, slowing the jumper down until he or she comes to a momentary stop at the bottom of the jump.
| Quantity | Symbol | SI Unit |
| kinetic energy | Ek | J |
| mass | m | kg |
| speed | v | m/s |
The kinetic energy of an object is equal to the work done to accelerate it.
 Read
Read
Read “Kinetic Energy” on pages 302 to 304 in your textbook.
 Self-Check
Self-Check
SC 5. Solve question 1 of “Practice Problems” on page 303 of your textbook.
 Self-Check Answers
Self-Check Answers
SC 5.
Given
mg = 45.0 kg
mb = 16.0 kg
v = 2.50 m/s
Required
the kinetic energy of the system (Ek)
Analysis and Solution
Find the total mass of the girl and bicycle system. Use the kinetic energy formula to find the answer.
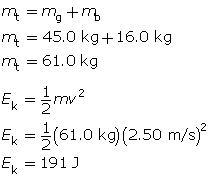
Paraphrase
The kinetic energy of the system is 191 J.
SC 6.
(a)
Given
k = 2500 N/m
x = 0.540 m
Required
the elastic potential energy stored in the bow (Ep)
Analysis and Solution
Use the elastic potential energy formula to find the answer.
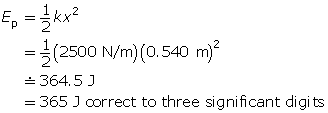
Paraphrase
The elastic potential energy stored in the bow is 365 J.
(b)
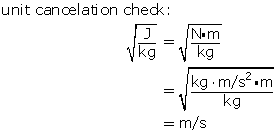
Given
m = 95.0 g
Ep = 365 J
Required
the speed of the arrow (v)
Analysis and Solution
Convert the mass of the arrow to kg.
![]()
All of the potential energy is converted to kinetic energy. Rearrange the kinetic energy formula to solve for the speed.
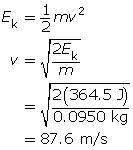
Paraphrase
The speed of the arrow is 87.6 m/s.
 Module 6: Lesson 1 Assignment
Module 6: Lesson 1 Assignment
Remember to submit the answers to TR 5, TR 6, and TR 7 to your teacher as part of your Module 6: Lesson 1 Assignment.
TR 5. A 25.0-N object is held 2.10 m above the ground. What is the potential energy of the object with respect to the ground?
TR 6. The kinetic energy of a 20.0-N object is 5.00 × 102 J. What is the speed of this object?
TR 7. A 10.0-N object is accelerated uniformly from rest at a rate of 2.5 m/s2. What is the kinetic energy of this object after it has accelerated a distance of 15.0 m?