Module 5—Circular Motion
 Lesson Summary
Lesson Summary
In this lesson you focused on the solution to this question:
- How are planetary and satellite motion explained using universal gravitation and the principles of circular motion?
Newton’s universal law of gravitation and the principles of circular motion can be applied to explain the observed motion of planets and satellites.
Equating the inward force and the universal law of gravitation gives an expression for the velocity of an orbiting planet or satellite.
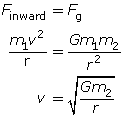
Equating Newton’s second law and the universal law of gravitation gives an expression for the inward acceleration of an orbiting planet or satellite.
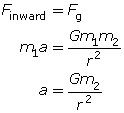
By determining the velocity and the acceleration of an orbiting planet or satellite, it is possible to explain the observed orbital motion, which is accurately described by Kepler’s three laws.
Lesson Glossary
periodic: recurring at regular intervals
trajectory: the path of a moving body through space