Module 5—Circular Motion
Kepler's Second Law
 Module 5: Lesson 3 Assignment
Module 5: Lesson 3 Assignment
Remember to submit the answers to TR 3 and TR 4 to your teacher as part of your Module 5: Lesson 3 Assignment.
 Try This
Try This
TR 3. Use the simulation to investigate Kepler's second law.
- Click the “Rewind” button (
 ).
).
- Click the “Data” button (
 ). Move the ellipse to the right so you can see it all by clicking in the ellipse and dragging it to the right.
). Move the ellipse to the right so you can see it all by clicking in the ellipse and dragging it to the right.
- Click the “Sweep” button (
 ). This will display sectors of equal area.
). This will display sectors of equal area.
- Click the “Play” button (
 ). “Pause” the planet (
). “Pause” the planet ( ), and use the “Step forward” button (
), and use the “Step forward” button ( ) to position the planet according to the following diagrams.
) to position the planet according to the following diagrams.
- Record the time display below each figure.
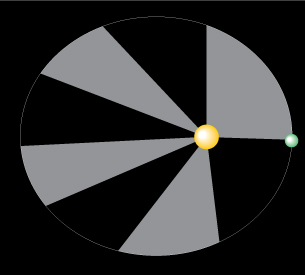
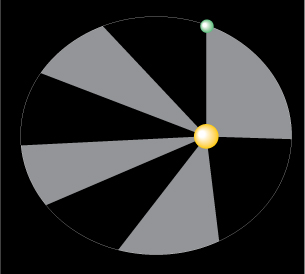
t1 = __________
t2 = __________
- Calculate the time interval for the planet to travel the sector (t2 − t1).
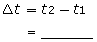
TR 4. Using the same method as in TR 3, measure the times required for the planet to traverse at least three of these sectors of equal area. Compare the time values. What do you observe?
Using Brahe's observations, Kepler provided an explanation of the answer to TR 4 in his second law.
Kepler's second law, the law of equal areas, stated that in equal time intervals, the radius vector from the Sun to a planet sweeps across equal areas. (This means that planets move fastest when they are closest to the Sun and slowest when they are farthest from the Sun.)
 Read
Read
To reinforce what you have discovered, read about Kepler’s first and second laws on pages 269 and 270 of the textbook.
 Watch and Listen
Watch and Listen
Watch this video about Kepler’s discovery.