Module 5—Circular Motion
Kepler's First Law
 Module 5: Lesson 3 Assignment
Module 5: Lesson 3 Assignment
Remember to submit the answer to TR 1 to your teacher as part of your Module 5: Lesson 3 Assignment.
 Try This
Try This
TR 1. Use the simulation to investigate Kepler's first law.
- Click the “Reset” button (
 ).
). - Using the eccentricity slider, set the eccentricity (e) to 0.400.
- Using the semi-major axis slider (mean distance between the planet and the Sun), set a to 2.0 AU.
- Click the “Play” button (
 ), and observe the planet (green) orbiting the Sun (yellow).
), and observe the planet (green) orbiting the Sun (yellow).
Draw the shape of the orbit and the location of the Sun relative to the orbit.
Based on the most precise observations available at the time—made by the astronomer Tycho Brahe—Kepler described the orbits of all planets in his first law.
Kepler's first law, the law of elliptical orbits, stated that the orbit of a planet around the Sun is an ellipse, with the Sun located at one of the two focal points of the ellipse.
You might want to think of an ellipse as a circle that has been stretched about an axis of symmetry. The classical geometrical way of describing an ellipse will prove more useful in this lesson.
Defining the Ellipse and Focal Points
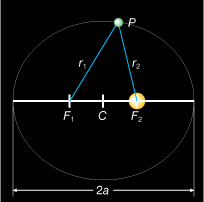
An ellipse is a curve on a plane. Each point, P, has a special relationship with two fixed points, F1 and F2. The sum of distances r1 and r2 from P to two fixed points, F1 and F2, is constant. The fixed points, F1 and F2, are the focal points of the ellipse. The sum of distances r1and r2 obeys the rule r1 + r2 = 2a, where 2a is the length of the major axis of the ellipse (the longest orbital diameter of the ellipse).
 Self-Check
Self-Check
SC 2. Answer the following using the definitions above and the given values of r1 and r2 for the ellipse shown. Remember that 1 AU = 1.496 × 1011 m.
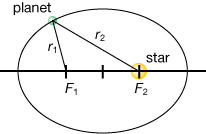
r1 = 1.736 × 1011 m
r2 = 2.543 × 1011 m
- The longest mean orbital diameter (major axis) of the planet’s orbit is ______________ m.
- The mean orbital diameter expressed in astronomical units is _____________ AU.
 Self-Check Answers
Self-Check Answers
SC 2.
- 2a = r1 + r2
= 1.736 × 1011 m + 2.543 × 1011 m
= 4.279 × 1011 m
The longest mean orbital diameter (major axis) of the planet’s orbit is 4.279 x 1011 m.
The mean orbital diameter expressed in astronomical units is 2.860 AU.
 Module 5: Lesson 3 Assignment
Module 5: Lesson 3 Assignment
Remember to submit the answer to TR 2 to your teacher as part of your Module 5: Lesson 3 Assignment.
 Try This
Try This
TR 2. Answer the following using the definitions above and the given values of r1 and r2 for the ellipse shown.

r1 = 1.396 × 1011 m
r2 = 2.432 × 1011 m
- The longest mean orbital diameter (major axis) of the planet’s orbit is ____________ m.
- The mean orbital diameter expressed in astronomical units is _____________ AU.