Module 4—Gravitational Force
 Module Summary
Module Summary
In this module you have studied some ways of applying Isaac Newton's laws, and you have learned about his law of universal gravitation. You saw how this law can help you explain the motions of astronomical objects.
People often confuse the terms weight and mass. Remember that mass is a measure of the amount of matter that makes up an object, whereas weight is a product of mass and the acceleration due to gravity.
Weight is expressed in the following equation:
![]()
Quantity |
Symbol |
SI Unit |
weight |
N |
|
mass |
m | kg |
acceleration due to gravity |
m/s2 |
You can use Newton's law of universal gravitation to help you understand how gravitational fields function. The field strength (g) increases as you approach the mass. For Earth, the maximum force is 9.81 m/s2 directed toward the centre of Earth. The field strength (g) obeys an inverse square law ![]() and extends outwards, affecting the motion of all objects that encounter it.
and extends outwards, affecting the motion of all objects that encounter it.
Newton’s law of universal gravitation states that the gravitational force of attraction between any two masses is proportional to the product of the two masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Expressed as an equation, it is as follows:
![]()
Quantity |
Symbol |
SI Unit |
force of gravity |
Fg |
N |
mass |
m |
kg |
separation between centres of masses |
r |
m |
gravitational constant |
G |
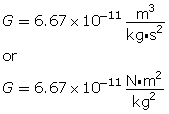 |
You can use Newton's law of universal gravitation to find the following:
- an object’s weight at any point relative to the source of the gravitational field
- the acceleration due to gravity at any point relative to the source of a gravitational field
- the force of attraction between any two masses
By measuring the force of attraction between two masses using a torsion balance, Henry Cavendish determined the value for the gravitational constant (G).
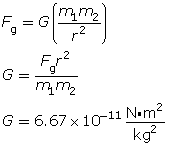
This let Cavendish calculate the mass of Earth. Start with the equation ![]() , and solve it for mass
, and solve it for mass 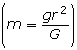 .
.
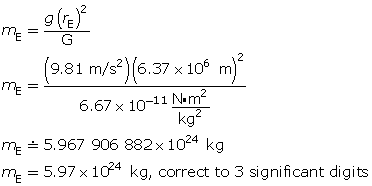
Cavendish experimentally verified Newton's law of universal gravitation and, in doing so, enabled us to understand gravitational fields beyond the surface of Earth. This will help you as you continue on to the next module.
 Module Assessment
Module Assessment
The assessment for Module 4 consists of three (3) assignments, as well as a final module inquiry project.
- Module 4: Lesson 1 Assignment
- Module 4: Lesson 2 Assignment
- Module 4: Lesson 3 Assignment
- Module 4 Project
Module 4 Project
The Module 4 Project is to choose one of the following items from your Physics 20 course folder:
- Going Beyond item from Lesson 1
- Reflect on the Big Picture item from Lesson 2
- Reflect on the Big Picture item from Lesson 3
You are then to submit your one item to your teacher for grading. Along with the item from the course folder, include an explanation about why you chose that particular item to submit.