Module 3—Effects of Force on Velocity
 Read
Read
What influences the coefficient values for static friction and kinetic friction? Read pages 180 to 184 of your textbook to learn more. The lug tread shown on page 184 has more traction in soft soil than the ribbed tread. Even the composition of the rubber makes a difference. For example, the rubber used for making winter tires is softer than the rubber used for summer tires.
 Self-Check
Self-Check
SC 1.
- Which of the materials listed in “Table 3.4” on page 183 of your textbook has the second highest coefficient of static friction?
- Which of the materials listed in “Table 3.4” has the lowest coefficient of kinetic friction?
 Self-Check Answers
Self-Check Answers
SC 1.
- Rubber on dry asphalt has the second highest coefficient of static friction.
- The curling stone on ice has the lowest coefficient of kinetic friction.
Determining the magnitude of the force of friction depends on the situation. Common examples and problem-solving methods are presented below.
Example Problem 1
The coefficient of kinetic friction between a block and the level surface it slides on is 0.45. If the mass of the block is 10.0 kg, what is the magnitude of the force needed to keep the block moving with uniform motion?
Solution
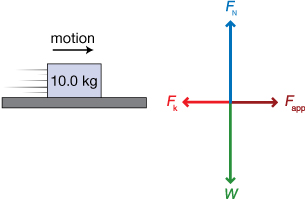
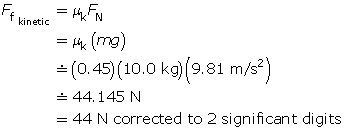
The applied force must balance the kinetic frictional force in order to maintain uniform motion. The magnitude of the force needed to keep the block moving with uniform motion is 44 N.
Example Problem 2
A student pulls on a 5.00-kg object and discovers that she needs to exert 30.0 N of force before the object moves. What is the coefficient of static friction between the object and the surface on which it rests?
Solution
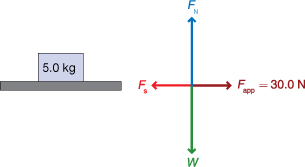
Since the applied force is 30.0 N just before moving, the frictional force must be equal in magnitude to the applied force. Therefore,
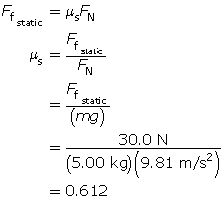
The coefficient of static friction is approximately 0.612.
Example Problem 3
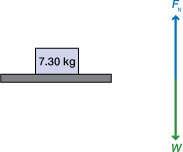
A 7.30-kg box is at rest on a level table. The coefficient of static friction between the box and table is 1.03. How big is the static frictional force?
Solution
 Try This
Try This
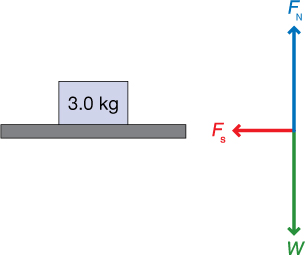
TR 2. Devise a method to determine the coefficient of static friction used in the simulation. Explain how you found the coefficient, and give its value.
TR 3. A student drew a free-body diagram for a box sitting at rest on the floor. Explain what is wrong with this diagram.
 Read
Read
“Example 3.17” on page 185 of your textbook shows how to determine mass from frictional forces on a sled, and “Example 3.19” on pages 187 and 188 of your textbook shows how to determine acceleration of a skidding vehicle. Use the two examples to help solve the following Self-Check question.
 Self-Check
Self-Check
SC 2. Go to page 190 of your textbook and complete question 6 of “3.5 Check and Reflect.”
 Self-Check Answer
Self-Check Answer
SC 2.
Given
![]() 2350 N [down]
2350 N [down] ![]() = 0.7
= 0.7
Required
the force of kinetic friction (![]() )
)
Analysis and Solution
The normal force will be equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the weight of the bike. The force of kinetic friction will be opposite to the direction of motion.
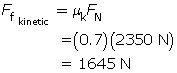
= 2 kN to 1 significant digit
Paraphrase
The force of kinetic friction is 2 kN [opposite to the direction of motion].
 Module 3: Lesson 3 Assignment
Module 3: Lesson 3 Assignment
Remember to submit the answers to TR 4 and TR 5 to your teacher as part of your Module 3: Lesson 3 Assignment.
 Try This
Try This
TR 4. The coefficient of static friction between a book and the level surface it slides on is 0.65. If the mass of the book is 2.0 kg, what minimum initial applied force is required to slide the books across the surface?
TR 5. An engine provides 5.0 kN of force to keep a 1600-kg vehicle moving at a uniform speed. (Air resistance is negligible.) What is the coefficient of rolling friction between the tires and the road surface?
 Self-Check
Self-Check
© 2007 Jupiterimages Corporation
SC 3. A 100.0-kg crate is at rest in the back of a truck. If the coefficient of static friction between the crate and the truck bed is 0.30, what is the maximum acceleration that the truck can have before the crate begins to slide? Draw a free-body diagram, and explain what force causes the crate to accelerate along with the truck.
 Self-Check Answer
Self-Check Answer
SC 3. The direction of the truck and the force arrows may be reversed.
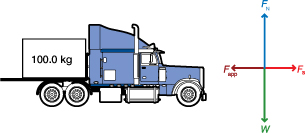
If the box does not slide on the truck bed, then the maximum acceleration is determined by the maximum static frictional force.
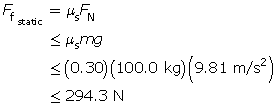
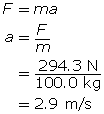
The maximum acceleration of the truck without the box sliding is 2.9 m/s2.
 Module 3: Lesson 3 Assignment
Module 3: Lesson 3 Assignment
Remember to submit the answer to the Reflect and Connect to your teacher as part of your Module 3: Lesson 3 Assignment.