Module 2—Motion in Two Dimensions
 Read
Read
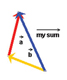
In paddling a canoe across a river, as shown in the example in the Get Focused, both the river and the canoe had velocities. How do you get the value of the resultant velocity? Read “Adding Two-dimensional Vectors Graphically” on pages 80 and 81 in your textbook to see the steps used in the tip-to-tail method to find the numerical value of the resultant of two vectors.
To see how this works in a practical problem of air speed in a plane flight so that you can do it yourself, open the Adding Vectors Graphically simulation. You will need to use a ruler, a pencil, an eraser, a protractor, and a sheet of lined paper as you follow along with the simulation.
 Module 2: Lesson 1 Assignment
Module 2: Lesson 1 Assignment
Remember to submit the answer to TR 1 to your teacher as part of your Module 2: Lesson 1 Assignment.
 Try This
Try This
TR 1. Using the tip-to-tail method of vector addition, complete “2.2 Check and Reflect” question 8 on page 90 of your textbook.
 Read
Read
What happens if you have to add more than two vectors? Read the last third of page 81 and the first half of page 82 in your textbook to see an example of how the tip-to-tail method is used to find the numerical value of the resultant of more than two vectors.
 Self-Check
Self-Check
SC 1. Complete practice problem 2 on page 82 of your textbook.
 Self-Check Answer
Self-Check Answer
SC 1.
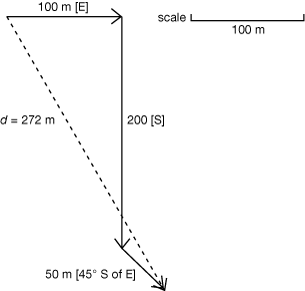
The student’s final position is 272 m [60° S of E].
Method 2: Parallelogram
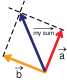
Some people prefer to use the parallelogram method instead of the tip-to-tail method. Either method works. Although the textbook uses the tip-to-tail method, see what you think of the parallelogram method.
Re-open the Vector Addition: Graphical simulation; then continue with the procedure.
Procedure
The simulation will be used to demonstrate the parallelogram method of vector addition.
-
If the screen is not empty, clear it by pressing the “Reset” button (
 ).
).
-
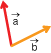
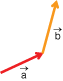
Draw two vectors in the window. The simulation will label the two vectors
 .
.
-
Join the two vectors tail end to tail end. Think of these two vectors as spanning a parallelogram—for example, forming two sides of a parallelogram whose other two sides still need to be constructed.
-
The simulation allows you to draw the remaining two sides of the parallelogram with dotted lines. The resultant vector goes from the point where the tail ends of the vectors join to the opposite corner of the parallelogram. To make sure that the dotted lines are parallel to the given vectors, draw the lines initially on top of the two vectors. Then move them into their correct positions by making them intersect the tips of the respective vectors.
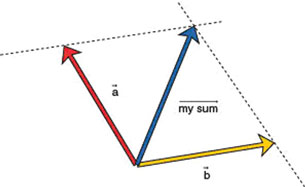
-
Finally, you can compare your resultant to the correct resultant drawn by clicking on the “Answer” button (
 ) in the simulation as described at the end of the section on the tip-to-tail method.
) in the simulation as described at the end of the section on the tip-to-tail method.
Observations and Analysis
 Module 2: Lesson 1 Assignment
Module 2: Lesson 1 Assignment
Remember to submit the answer to LAB 3 to your teacher as part of your Module 2: Lesson 1 Assignment.
LAB 3. Complete the following steps.
-
Step 1: Draw the parallelogram for the vectors in the top row of the table.
-
Step 2: Draw the resultant for the vectors in the top row of the table.
-
Step 3: Draw the resultant for the vectors in the bottom row of the table using the tip-to-tail method.
Examples of the parallelogram method and tip-to-tail method have been provided.
| Parallelogram Method | Example: |
a.
|
b.
|
c.
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tip-to-Tail Method | Example:
|
d. |
e.
|
f.
|
Method 2 Summary
How can vectors be added using the parallelogram method of vector addition?
Vectors are added by placing the tail of the two vectors together and completing the parallelogram these two vectors define. The sum (resultant) is the vector that shares these vectors’ tails and the opposite vertex of the parallelogram.
 Self-Check
Self-Check
SC 2. Refer to LAB 3 in order to answer the following questions.
- What do you notice about the magnitude and direction of each vector
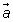 in the bottom (tip-to-tail method) row of Lab 3 compared to the vector
in the bottom (tip-to-tail method) row of Lab 3 compared to the vector 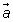 in the table just above it?
in the table just above it?
- What do you notice about the magnitude and direction of each vector
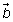 in the bottom (tip-to-tail method) row of Lab 3 compared to the vector
in the bottom (tip-to-tail method) row of Lab 3 compared to the vector 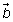 in the table just above it?
in the table just above it?
-
What do you notice about the magnitude and direction of each resultant vector in the bottom (tip-to-tail method) row of Lab 3 compared to the resultant vector in the table just above it?
-
Are the magnitude and direction of the resultant vector different if you use the tip-to-tail method instead of the parallelogram method?
-
Which method do you prefer to use? Explain why.
 Self-Check Answers
Self-Check Answers
SC 2.
-
The magnitude and direction of each vector
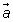 in the bottom row is the same as the vector
in the bottom row is the same as the vector 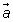 in the table just above it.
in the table just above it.
-
The magnitude and direction of each vector
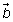 in the bottom row is the same as the vector
in the bottom row is the same as the vector 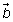 in the table just above it.
in the table just above it.
-
The magnitude and direction of the resultant vector in the bottom row is the same as the magnitude and direction of the resultant vector in the table just above it.
-
The magnitude and direction of the resultant vector is the same with either method.
-
Choices and reasons will vary. The text only uses the tip-to-tail method, which works for both collinear and non-collinear vectors.
 Module 2: Lesson 1 Assignment
Module 2: Lesson 1 Assignment
Remember to submit the answers to Reflect and Connect to your teacher as part of your Module 1: Lesson 2 Assignment.