Complete the Lesson 4 Assignment that you saved in your course folder at the beginning of this lesson.
![]() Save your responses in your course folder.
Save your responses in your course folder.
Go to Module 8 Project: Creating the Ultimate Password. Complete Activity 4: Tricky Passwords. Also complete the Conclusion.
![]() Save your responses in your course folder. When you are finished, submit the entire project to your teacher.
Save your responses in your course folder. When you are finished, submit the entire project to your teacher.
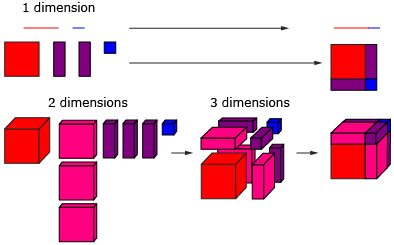
The binomial theorem can be explained geometrically up to a power of 3. Explain how the following is representative of the binomial theorem. If you need help, open Going Beyond Hint.
![]() Save your responses in your course folder.
Save your responses in your course folder.