Explore
In Share 1, one of your group members may have suggested using a diagram to solve the PIN problem. The following diagram is called a tree diagram.
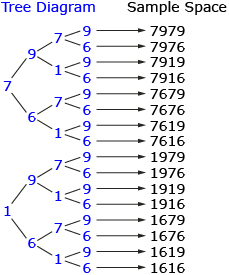
By counting the total number of terminal branches in the tree diagrams, you can see that Abdy has a choice of 16 different PINs. The list of all 16 possible PINs is called the sample space for this problem. The sample space is a list of all possible outcomes. You could also list all possible outcomes in an outcome table, such as the following one.
| First Digit | Second Digit | Third Digit | Fourth Digit |
| 7 | 9 | 7 | 9 |
| 7 | 9 | 7 | 6 |
| 1 | 9 | 7 | 9 |
| 1 | 9 | 7 | 6 |
| 7 | 6 | 7 | 9 |
| 7 | 6 | 7 | 6 |
| 1 | 6 | 7 | 9 |
| 1 | 6 | 7 | 6 |
| 7 | 9 | 1 | 9 |
| 7 | 9 | 1 | 6 |
| 1 | 9 | 1 | 9 |
| 1 | 9 | 1 | 6 |
| 7 | 6 | 1 | 9 |
| 7 | 6 | 1 | 6 |
| 1 | 6 | 1 | 9 |
| 1 | 6 | 1 | 6 |

die toss:Hemera/Thinkstock, coin toss: iStockphoto/Thinkstock
Read through Mathematics Glossary Tree Diagram to see how all possible outcomes of tossing a penny and rolling a die can be calculated by using a tree diagram. As you read, note that the order of tossing the penny or rolling the die does not affect the outcomes or sample space. Read the first example only in Mathematics Glossary Tree Diagram.
In Try This 2 you will find possible outcomes using tree diagrams and outcome tables. You will then determine an expression to calculate these outcomes.