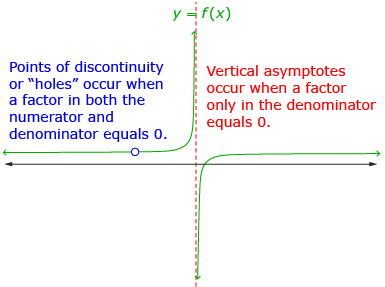
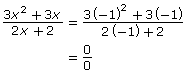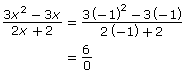The main difference between the two functions in Try This 2 is that the non-permissible value for one produced a point of discontinuity and the other produced an asymptote.
| When a factor that occurs in both the numerator and denominator is equal to 0 | When a factor that occurs only in the denominator is equal to 0 | |
| Function | ||
| Non-permissible Values | x = −1
|
x ≠ −1
|
| Type of Non-permissible Value | indeterminate | undefined |
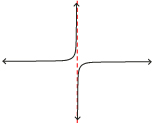
| Appearance on Graph | hole or point of discontinuity
|
asymptote
|
| Factored Form | 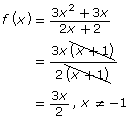 |
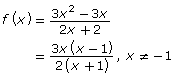 |
Common Factors
|
Yes, a factor in the numerator and in the denominator causes a hole. | No, a factor only in the denominator causes an asymptote. |
A formal definition of division is ![]() if and only if a = bc. A division by 0 fails this definition. If you begin with
if and only if a = bc. A division by 0 fails this definition. If you begin with ![]() , then a = 0c also needs to be true—it is not for any a ≠ 0. This is why a division by 0 is usually said to be undefined.
, then a = 0c also needs to be true—it is not for any a ≠ 0. This is why a division by 0 is usually said to be undefined.
An exception occurs when a = 0. This gives ![]() , or 0 = 0c, which is true for any c. By this definition,
, or 0 = 0c, which is true for any c. By this definition, ![]() is equal to any value.
is equal to any value. ![]() is often referred to as indeterminate.
is often referred to as indeterminate.
You do not need to understand indeterminate values for this course. You only need to recognize that indeterminate values will cause points of discontinuity to appear on the graph of a rational function.