Explore
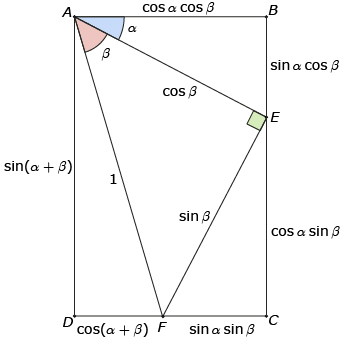
In Try This 1 you may have drawn a diagram similar to the diagram shown here.
By recognizing that AD = BE + CE, you can predict the identity sin (α + β) = sin α cos β + cos α sin β. Similarly, because AB = DF + CF, cos α cos β = sin α sin β + cos (α + β). This second identity is often rewritten as cos (α + β) = cos α cos β − sin α sin β. These two identities are called sum identities. In Try This 2 you will use the sum identities to predict other identities.
Try This 2
- Explain why sin (−x) = −sin x and cos (−x) = cos x are identities.

-
Use the sum identity sin (A + B) = sin A cos B + cos A sin B, and the identities from question 1 to show that sin (A − B) = sin A cos B − cos A sin B.


- Using a procedure similar to that of question 2, predict an identity for cos (A − B).



-
Consider the special case where A = B for the identities sin (A + B) = sin A cos B + cos A sin B and cos (A + B) = cos A cos B − sin A sin B. Write simplified equivalent expressions for sin 2A and cos 2A.



![]() Save your answers in your course folder.
Save your answers in your course folder.