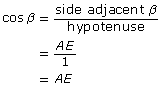Discover
Try This 1
Open Sum Identity, which shows a rectangle ABCD, where BC < 2AB. E is a point on BC and F is a point on CD such that ∠AEF is a right angle. ∠BAE has been labelled α (alpha) and ∠EAF has been labelled β (beta).

- Set point E to a position you like and sketch the diagram on a full piece of paper. Use the measures of α and β to determine the rest of the angles in the diagram.

Click the “Show angles” box in Sum Identity to check your values. -
- Explain how you know ∠CEF = α.
-
Determine an expression for each of the acute angles in the diagram in terms of α and β. Label each angle in your diagram.

-
The hypotenuse AF of the inscribed right triangle has a length of 1 unit. Explain why the length of AE can be represented as cos β. Label AE as cos β.

- Determine an expression for line segment AB in terms of sin α, cos α, sin β, and cos β. (You will not need all of these.) Write this expression on your diagram.
Click the “Show AE and AB lengths” box in Sum Identity to check your expression. - Determine expressions for BE, EF, CE, CF, AD, and DF in terms of sin α, cos α, sin β, and cos β. Label each side length on your diagram using these sines and cosines.
Click the “Show all lengths” box to check your diagram. -
-
Which angle in the diagram, other than ∠BAF, is equal to α + β?
-
AD = BE + EC. Use this fact to determine a trigonometric identity that relates the two side lengths.
- Predict another identity using the fact that AB = DC.
-
![]() Save your answers in your course folder.
Save your answers in your course folder.
Share 1
With a partner or group, discuss the following questions based on your responses to Try This 1.
- Verify your possible identities from parts 6.b. and 6.c. numerically using values of α and β.
- Does each identity apply to angles that are obtuse? Are there any restrictions on the domain? Describe your findings.
![]() If required, save a record of your discussion in your course folder.
If required, save a record of your discussion in your course folder.