Lesson 4 Summary
It is possible to perform multiple transformations on a function. The order in which you apply the transformations is important in determining the resulting function. The form of the equation of the function described in the diagram is commonly used when transforming a function, as the different parameters are easily interpreted. Using this form implies that the function is stretched and reflected before it is translated.
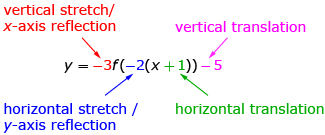
Multiple Transformations reviews how some specific functions of the form ![]() behave when you change the different parameters.
behave when you change the different parameters.

In Lesson 5 you will begin to explore the idea of reversing a function.