Lesson 1 Summary
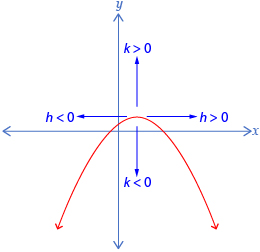
A transformation is a change in the shape or position of a figure or relation. A translation is a type of transformation that causes a “slide” in the graph. The new graph is the same size, shape, and orientation as the original but in a different position.
In a graph of the form y − k = f(x − h), k is the vertical translation from y = f(x). If k > 0, the translation is upwards. If k < 0, the translation is downwards.
In a graph of the form y − k = f(x − h), h is the horizontal translation from y = f(x). If h > 0, the translation is to the right. If h < 0, the translation is to the left.
You may find it useful to keep a summary of the different transformations you learn in this module using a table similar to the following.
| Parameter | Type of Transformation | Effect on Graph |
In the next lesson you will begin to look at reflections of a function.