Art History
A look to the past guides in the future.
Prehistoric to Roman Times
30,000 to 10,000 BC
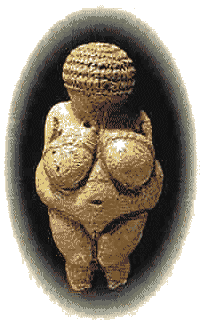
During the Paleolithic Period or Old Stone Age, cave paintings, like the one from the Cave of Lasaux in France, and small sculptures like Venus of Willendorf c30,0000 - 25,000 B.C.. (a limestone fertility drawing of a woman with exaggerated bits) begin popping up in places like present day France and Spain
10,000 to 8,000 BC
The Mesolithic Period Middle Stone Age sees people begin to settle in pseudo-farming communities. Cliff faces become canvases as people who are driven by thoughts of magic and hunting paint with dirt and animal fat.The paintings at Castellon are located in a rocky gorge.
8,000 to 3,000 BC
As the New Stone Age or the Neolithic Period arrives; folks are living in village-like settings. they grow things and keep animals within their sight as simple architectural structures are built and richly decorated pottery is created. Stonehenge and other megaliths (big things) are constructed in what is now England and Scotland. Prehistoric art continues in various parts of the globe including North and South America.
3,000 to 331 BC
In Mesopotamia (roughly between present day Iran and Turkey) people construct ziggurats (palaces) as bronze sculptures, rock carvings and wooden musical instruments adorned with gold are created. Sumerians, Assyrians and Persians leave their artistic mark as they float in and out of the area.
3.200 to 1070 BC
In the land we call Egypt, people with a strong belief in the afterlife create paintings and elaborate sculptures to decorate tombs. The Great Sphinx is constructed from sandstone while limestone forms the base of the pyramid and temples.
3,000 to 1,000 BC
The Minoans on the Island of Crete and the Mycenaeans of Greece create what we now call Aegean art. Gorgeous wall murals, and dazzling ceramic ware are created in between natural disasters and wars.
800 to 323 BC
After creating simplified kouros (male) and kore (female) figures, the Greeks go wild portraying perfectly proportioned bodies of young men and women. The Parthenon is built, columns have personality and vase painting flourishes.
323 to 150 BC
The Hellenistic Period begins when Alexander the Great expires and his empire is liquefied. the art of this time is symbolic of the breakdown as pain, suffering, ecstasy and some other emotions are expressed. Later the Etruscans fabricate pottery and sculpture as funerary offerings- not unlike the Egyptians.
509 BC to 337 AD
The Romans conquer Greece and proceed to lop off the heads of many Greek sculptures. Even so, the Romans appreciate the art of Greece and begin to "borrow" their artistic concepts. Large scale works are seen, as are mosaics, fresco paintings and arches.
During the Paleolithic Period or Old Stone Age, cave paintings, like the one from the Cave of Lasaux in France, and small sculptures like Venus of Willendorf c30,0000 - 25,000 B.C.. (a limestone fertility drawing of a woman with exaggerated bits) begin popping up in places like present day France and Spain
 |
 |
| Cave of Lascaux |
Venus of Willendorf |
10,000 to 8,000 BC
The Mesolithic Period Middle Stone Age sees people begin to settle in pseudo-farming communities. Cliff faces become canvases as people who are driven by thoughts of magic and hunting paint with dirt and animal fat.The paintings at Castellon are located in a rocky gorge.
 |
 |
| Hand Prints Castellon, Spain |
Deer Hunt Castellon, Spain |
8,000 to 3,000 BC
As the New Stone Age or the Neolithic Period arrives; folks are living in village-like settings. they grow things and keep animals within their sight as simple architectural structures are built and richly decorated pottery is created. Stonehenge and other megaliths (big things) are constructed in what is now England and Scotland. Prehistoric art continues in various parts of the globe including North and South America.
 |
 |

|
| Women and Animals Facsimilie Cogul, Lerida, Spain c. 4000-3000 BC (BCE) Museo Arqueologico, Barcelona |
Tomb Interior with Corbeling and Engraved Stones Newgrange, Ireland c. 3000 - 2500 BC (BCE) |
Stonehenge, Salisbury Plain Wilshire, England c. 2750-1500 BC (BCE) |
3,000 to 331 BC
In Mesopotamia (roughly between present day Iran and Turkey) people construct ziggurats (palaces) as bronze sculptures, rock carvings and wooden musical instruments adorned with gold are created. Sumerians, Assyrians and Persians leave their artistic mark as they float in and out of the area.
 |
 |
 |
3.200 to 1070 BC
In the land we call Egypt, people with a strong belief in the afterlife create paintings and elaborate sculptures to decorate tombs. The Great Sphinx is constructed from sandstone while limestone forms the base of the pyramid and temples.
 |
 |
3,000 to 1,000 BC
The Minoans on the Island of Crete and the Mycenaeans of Greece create what we now call Aegean art. Gorgeous wall murals, and dazzling ceramic ware are created in between natural disasters and wars.
 |
 |
| Minoan |
Mycenaean - the chanting priest |
800 to 323 BC
After creating simplified kouros (male) and kore (female) figures, the Greeks go wild portraying perfectly proportioned bodies of young men and women. The Parthenon is built, columns have personality and vase painting flourishes.
 |
 |
 |
| The Discus Thrower |
Venus de Milo |
Zeus |
323 to 150 BC
The Hellenistic Period begins when Alexander the Great expires and his empire is liquefied. the art of this time is symbolic of the breakdown as pain, suffering, ecstasy and some other emotions are expressed. Later the Etruscans fabricate pottery and sculpture as funerary offerings- not unlike the Egyptians.
 |
 |
509 BC to 337 AD
The Romans conquer Greece and proceed to lop off the heads of many Greek sculptures. Even so, the Romans appreciate the art of Greece and begin to "borrow" their artistic concepts. Large scale works are seen, as are mosaics, fresco paintings and arches.