The 9 Elements of Digital Citizenship
| Site: | Joans-place |
| Course: | E-learning Strategies |
| Book: | The 9 Elements of Digital Citizenship |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Saturday, 18 October 2025, 11:27 AM |
Description
9 Elements
Overview
![]() Making connections to the Real World:
Making connections to the Real World:
- How does Digital Citizenship
apply in an e-Learning environment? - What value does this content have to you in your life? Why are We learning this?
Assignments:
- Digital Citizenship Scenario
Mike Ribble and Gerald Bailey have provided the framework in understanding Digital Citizenship, which includes the following 9 Elements:
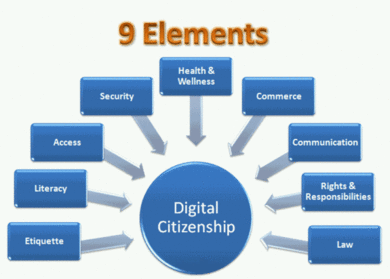
Through developing an understanding of what each of these elements mean you can determine how these elements influence how you connect with and use technology.
Digital Access
 An increasing number of people believe that is it important that all citizens (local and global) have sufficient access to technology, or they may be at a disadvantage when working in the "real world". Some questions that may arise from the topic of Digital Access may include:
An increasing number of people believe that is it important that all citizens (local and global) have sufficient access to technology, or they may be at a disadvantage when working in the "real world". Some questions that may arise from the topic of Digital Access may include:
- How do all citizens gain access to technology instead of few or many?
- Whose responsibility is it to ensure access is provided and available?
- How do students receive access to technology in appropriate learning settings at school?
- Do those who have special needs or interests have access to the technology needed that best helps them learn?
- Should high speed internet be considered a basic human right or human need in today's society?
- Are those citizens (local and global) who do not have access disadvantaged in any way?
Digital Access represents: hardware, internet access as well as access to software needed for creativity, productivity and function.
Digital Commerce

Digital Commerce refers to the buying and selling of goods online, or through the use of locating goods to buy or sell via the internet. Some feel that this may not be a relevant topic if you do not yet have a
|
Digital Communications
We live in an increasingly digital world and we have so many communication tools at our fingertips (texting, social online media, cell phones, blogs, wikis, podcasts...). While many are actively using various communication tools it is important to remember:
- who is your audience?
- What method of communication is most appropriate (not always easiest) for a given situation?
- How does your language, text or symbols fit the circumstance. For example when writing a formal piece of writing it would not be appropriate to use Instant Messaging Acronyms.
Non-Academic Uses of Technology
It is likely that you will spend time online sending emails, writing a personal blog, playing online games, or visiting social networking sites like Facebook or Twitter.
The way you communicate on a social networking website will be significantly different than how you communicate within your e-learning courses.
Your information is private and secure in the e-learning environment, and any information you send directly to your teacher (Using Moodle Assignment feature) will be private between the two of you, and not shared with the rest of the classroom community. The same cannot be said for most non-academic uses of technology
Social Networking:
In the past few years have social networking sites become popular. Many people are taking advantage of this new way of communicating and staying in contact with friends, family and co-workers.
However, because of the public nature of these sites, users need to be cautious with their personal information.
-
Keep personal identifying information such as name, age, date of birth, address, phone number off social networking sites. When sending personal information, send it as a personal message, rather than as a general comment, because comments can be visible to everyone.
-
Become familiar with the privacy features on social networking sites. Only people that know you in real life should have access to
your profile . Understand how to control privacy settings. Most online journals, blogs, instant messages and social networking sites have privacy settings that determine who can and can't view a user's profile and information. -
Be cautious when posting photographs.
Photos can easily be removed and used by third parties - once it is posted to the internet, you will never be able to completely delete it. Be mindful of how aphoto represents you.
Instant Messaging / Texting / Mobile Devices:
Social Networking and internet-based activities are not exclusively accessed on desktop / laptop computers. Many students have cellphones or other mobile devices that can connect to the internet.
-
Only give your cell phone number to people you know and trust. Do not post your cell phone number online. Never give out anyone else's number without permission.
-
Never take
pictures of anyone with your cell phone or camera and post on the internet without their permission. -
Never reply to a text message or open an attachment from people you do not know. If in doubt, delete the file.
Digital Literacy
 Digital Literacy involves having the skills necessary to be able to know:
Digital Literacy involves having the skills necessary to be able to know:
- Basic computing skills that transfer from program to program
- How to choose one program or method to best suit your need or purpose
- How to be a critical thinker in relation to the information you come across online:
- Is it biased? Credible? Sourced? Accurate?
- how does information located compare with other sources of information?
- Are they an expert on the topic?
- How to locate information needed with ease and in an efficient manner
Digital Literacy is more than just being comfortable in playing to figure something out (which is also an important skill), but having the knowledge of how to apply skills to the task that you are wanting to complete in an efficient and suitable manner. It is having a digital toolkit of skills that can be transferred to other digital tasks and being knowledgeable about asking the right questions as you look for information online.
Digital Etiquette
 Digital Etiquette is what most people think of when they think of Digital Citizenship. Etiquette can be the following:
Digital Etiquette is what most people think of when they think of Digital Citizenship. Etiquette can be the following:
- How others interact with one another digitally (kind or hurtful)
- How others digital interactions affect another individual (distraction to self or others from another task such as watching a movie or driving)
- Understanding that what is posted online remains there permanently, even if you delete, so keeping in mind who your potential audience is will help you to determine if your actions, pictures or words are appropriate or not
Digital Law
 Digital Law is a very complex and
Digital Law is a very complex and
Quick Tips to Adhere to Academic Honesty & to Avoid Infringing on Copyright Laws:
- Students are expected to do their own work
- Cite any work from others that you have used within your work (includes oral, multi-media presentations and your writing)
- There are limits to the amount of material which can be copied without obtaining express permission from the original author, so it's important to only cite or reference material that's meaningful and relevant.There's no need to provide a full paragraph quotation from
a website or other source. Your teacher will be interested in your own ideas and impressions, not just information you can search on the internet.
- There are limits to the amount of material which can be copied without obtaining express permission from the original author, so it's important to only cite or reference material that's meaningful and relevant.There's no need to provide a full paragraph quotation from
- If you are using information music or images that others have created, you are to ask for their permission to use, or use creative commons
domain materials and cite these sources in your references also - Know what plagiarism is so you can avoid it:
-
Any of the following is plagiarism, without reference or acknowledgement of the original source, can be considered as plagiarism violations:
-
Direct duplication, by copying (or allowing to be copied)another person's work, from a book, article, web site, image, music, another student's assignment etc.
-
Paraphrasing of another person's work closely, making only minor changes to the wording but with the essential meaning, form or progression of ideas maintained.
-
Piecing together sections of the others' work into a new whole.
-
Submitting your own work which has already been submitted for assessment in another subject or course.
-
Producing assignments with other people (eg. Another student, a tutor) which is being assessed as your own independent work.
-
-
Tools That Teachers Can Use to Help Determine if Plagiarism has occurred:
Search Engines Such as Google
Teachers use search engines, like Google, to check students work against other, published sources. Teachers are familiar with sites like
Turnitin Turnitin is a program that is used to check student assignments against a secure database of student work. Each time a teacher submits a student's essay, it is checked against all other essays in the system, and is subsequently added into the database. All personally identifiable information is removed from the assignment, and no other teachers,students or users have direct access to the assignment. Turnitin can be used by students to check their work for any potential plagiarism issues arising from not referencing a source properly.Often, a student has honest intentions of using a reference properly, but doesn't understand the process or simply forgets to cite the website. With Turnitin, a student is assured their paper meets established guidelines |
Digital Rights & Responsibilities
 Digital Rights & Responsibilitiesincludes the most common aspect that most associate with Digital Citizenship. Often people are not aware that Digital Citizenship is more comprehensive than Rights & Responsibilities, as you are learning through this course there are 9 Elements that are incorporated within Digital Citizenship. Rights & Responsibilities are very important however and include topics such as:
Digital Rights & Responsibilitiesincludes the most common aspect that most associate with Digital Citizenship. Often people are not aware that Digital Citizenship is more comprehensive than Rights & Responsibilities, as you are learning through this course there are 9 Elements that are incorporated within Digital Citizenship. Rights & Responsibilities are very important however and include topics such as:
- Rights include adhering to the Charter of Rights and Freedoms in Canada as well as Freedom of Information and Protection of Privacy Act
- Students should be aware of both right that you have and responsibilities to go along with those rights. If your actions negatively impact anther's rights then you do not have a right to act in that manner- Digitally or face-to-face.
- The moment you interact online you are becoming a citizen within that digital community. How will your actions and voice promote you in a positive light, that demonstrates that you are a knowledgeable and positive citizen within that digital community? How will your actions or what you post (including images) impact another person today, tomorrow or years in the future?
When a person infringes anther's rights or safety it is considered to be bullying. However, if you, your friends and our society are proactive in teaching each other how to engage online in a positive way, contributing to and modeling good citizenship bullying would not occur. It is important to note that although the term cyber-bullying is used a lot in our society, the majority of bullying occurs face-to-face not digitally. Some feel that the focus o cyber bullying instead of focusing on how to teach rights and responsibilities to students and adults is reactionary and not preventative. How can we prevent bullying or inappropriateness from occurring online? By knowing our Rights and Responsibilities in how to contribute to the digital society in a positive way!
Digital Health & Wellness

- Physical: As you Learned in Lesson 1.4 through the ergonomics
video , the manner in which you set up your work station can affect your heath - Psychological: Technology addiction is a common issue in society and this includes those who cannot take a break from the use of technology as well as those who begin losing interest in friends, family and other things that used to interest them. Being aware of your technology use and your dependency will help you to curb the possible addictive affects. Technology is a tool for many different tasks that we wish to achieve, but it is not our life. How do you find a balance between technology and nature?
Digital Security
 When using technology it is important to ensure you know how to:
When using technology it is important to ensure you know how to:
Create a complex password so it can not be easily guessed- Keep your personal passwords private, they are not for anyone else. Being careful of where you keep your passwords is also important
- Protect your home and school networks from the likelihood of getting viruses or worms
These pieces above are all part of Digital Security
Identity Theft / Phishing:
Your personal data can be used in a malicious manner, and there are many scammers who pose as legitimate businesses and try to gain your information.
-
Be careful when giving out personal information, such as your phone number, home address, community name, full name or birth date. Be selective about the amount of information you reveal about yourself on the internet. Limit the data that you give out in contests or surveys.
-
Legitimate companies will not ask for sensitive information by e-mail. Asking for this information is illegal soliciting, known as "phishing”. You need to know how to protect yourself.
-
Use your best judgement when on the Internet. If it sounds too good to be true, it probably is.
-
Watch for emails that appear to be from a bank or
credit card company that ask forpersonal information, or ask you to call a phone number to verify your account information. -
Watch for emails with obvious spelling mistakes, or messages that are sent out to a large number of recipients.
-
Always use a complex password, and change it frequently. Make your password difficult to guess, and never share it with your friends.
-
Spam
Learn to recognize spam and delete it before reading and/or opening it.
-
Do not forward or respond to spam messages.
-
Watch for emails with obvious spelling mistakes.
-
Be wary of messages that are sent out to a large number of recipients.
-
Avoid clicking on suspicious email links. Not all links are legitimate and they may contain malicious codes like viruses or redirect you to undesirable sites.