On-line with Moodle
| Site: | Joans-place |
| Course: | Ideas from an On-line Educator |
| Book: | On-line with Moodle |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Friday, 31 October 2025, 3:08 PM |
Description
Understanding how Moodle is designed
Social Constructivism
This is a theory of learning that says that in order to learn new concepts, learners need to actively construct meaning in relating:what is already known to each other and to their own experiences.
In practice, learners will:
See topics as relevant
Plan & carry out work collaboratively
Practice self assessment
Apply concepts to new situations
Moodle was actually designed to support this approach to learning. It is a good idea to become familiar with using the official Moodle Site - Moodle.org
Educational Philosophy
An excellent quote to set the stage...
"Martin's background in education led him to adopt social constructionism as a core theory behind Moodle. This is revolutionary, as most CMS systems have been built around tool sets, not pedagogy. Most commercial CMS systems are tool-centered, while Moodle is learning-centered. Social constructiionism is based on the idea that people learn best when they are engaged in a social process of constructing knowledge through the act of construction of an artifact for others. That's is a packed sentence, so let's break it down a bit. The term 'social process' indicates that learning is something we do in groups. From this point of view, learning is a process of negotiating meaning in a culture of shared artefact's and symbols. The process of negotiating meaning and utilizing shared artefact's is a process of constructing knowledge. We are not blank slates when we enter the learning process. We need to test new learning against our old beliefs and incorporate them into out existing knowledge structure. Part of the process of testing and negotiating involves creating artefact's and symbols for others to interact with. We create artifacts and in turn negotiate with others to define the meaning of those artefact's in terms of a shared culture of understanding. So how does this relate to Moodle? The first indication is in the interface. While tool-centric CMSs give you a list of tools as the interface, Moodle builds tools into an interface that makes the learning task central. You can organize your model course by week, topic, or social arrangement. Additionally, while other CMS's support a content model that encourages instructors to upload a lot of static content, Moodle focuses on tools for discussion and sharing artifacts. The focus isn't on delivering information; it's on sharing ideas and engaging in the construction of knowledge. Moodle's design philosophy makes this a uniquely teacher-friendly package that represents the first generation of educational tools that are truly useful." ...directly from Using Moodle Cole & Foster O'Reilly 2008
Social Constructivism & Teaching Strategies
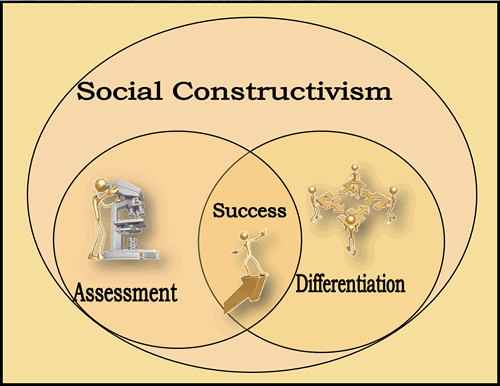
Social constructivism is the difference between a traditional approach and a project based approach to learning. The social constructivist philosophy is the difference between a lecture and a discussion.
The social constructivist philosophy believes that people learn best when:
- they interact with the learning material
- construct new material for others
- interact with other students about the material
...from Moodle 1.9 - E-learning Course Development Rice PACKT 2008
Why is Assessment important?
1. Assessment serves different purposes at different times: it may be used to
find out what students already know and can do; it may be used to help students improve their learning; or it may be used to let students and their parents know how much they have learned in s prescribed period of time.
2. Assessment must be planned and purposeful.
3. Assessment must be balanced, including oral, performance, and written tasks, and be flexible in order to improve learning for all students.
4. Assessment and instruction are inseparable because effective assessment informs learning.
5. For assessment to be helpful to students, it must inform them in words, not numerical scores or letter grades, what they have done well, what they havce done poorly, and what they need to do next to improve.
6. Assessment is a collaborative process that is most effective when it involves self-, peer and teacher assessment.
7. Performance standards are an essential component of effective assessment.
8. Grading and reporting student achievement is a caring, sensitive process that requires teachers' professional judgement.
Authentic vs Traditional Assessment
| Authentic Performing a Task Real-life Construction/Application Student-structured Direct Evidence |
Traditional Selecting a Response Contrived Recall/Recognition Teacher-structured Indirect Evidence |
| Assessment FOR learning | Assessment OF Learning |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
...from Talk About Assessment Damian Cooper Nelson 2007
What about Differentiation?
When students...
- find out about themselves as learners, they become more independent.
- start where they are, progress in learning is genuine and lasting.
- work on tasks at the appropriate level of challenge, they are neither frustrated nor bored, but motivated.
- study essential content, learning is richer and deeper.
- learn to appreciate differences, they work more collaboratively with their peers.
...from Start Where They Are Karen Hume
Traditional vs Differentiated Classroom
Traditional
|
Differentiated
|
... from Differentiation From Planning to Practice Wormeli Pembroke 2007
What about Brain Research?
"Moving down the pyramid, input changes to verbal and visual processing as 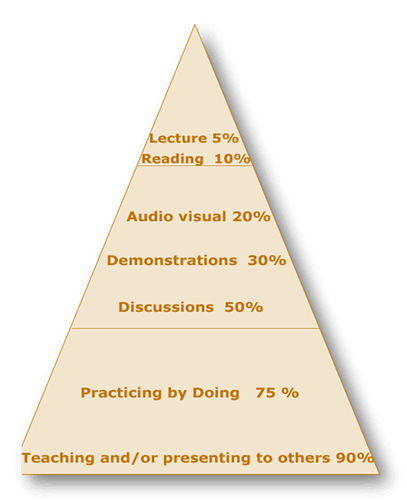
students become more involved in the learning process and retention increases.
The methods at the bottom of the pyramid involve having students doing something through practice and teaching others or using the new learning immediately.
We have known for a long time that the best way to learn something is to prepare to teach it.
In other words, whoever explains, learns."
From How the Brain Learns Sousa Sage Publications 2006
Universal Design for Learning
 The goal for every student is to learn, but not every child learns in the same way.Some students difficult time with traditional classroom materials.
The goal for every student is to learn, but not every child learns in the same way.Some students difficult time with traditional classroom materials.
Adaptations are being built into the distributed learning curriculum materials, using computer technology, to compensate for variation among their students.
Distributed learning helps to create choices in how learners present information, structure assignments, and demonstrate understanding.
Universal Design has its roots in architecture and urban planning. Ramps, automatic doors, and curb cuts were created to provide access to people with physical disabilities but actually ease access for everyone. Think of the last time you pulled a roll around suitcase and the broader value of ramps is instantly apparent.
access for everyone. Think of the last time you pulled a roll around suitcase and the broader value of ramps is instantly apparent.
The Three Principles
- Multiple Methods of Presentation
- Content is presented using multiple media, such as oral lectures, textbooks, charts, visuals, audio tapes or mp3s, interactive animations, podcasts, videos, wikis, and forums. Provides choice for students.
- Multiple Options for Participation
- Allows flexibility in how students interact with the material and they can choose their preferred method of learning new material.
- Materials encourage students to add their own words, images, audio, video, and ideas and share them with their peers to construct learning
- Multiple Means of Expression
- Assignments are accepted in various formats. A student who finds
written expression difficult might show his knowledge orally; another might turn in a report, write a play, create a web site or develop a project to demonstrate learning.
...from Teaching Every Student in the Digital Age Rose & Meyer 2002